Duties of a Social Worker in Healthcare
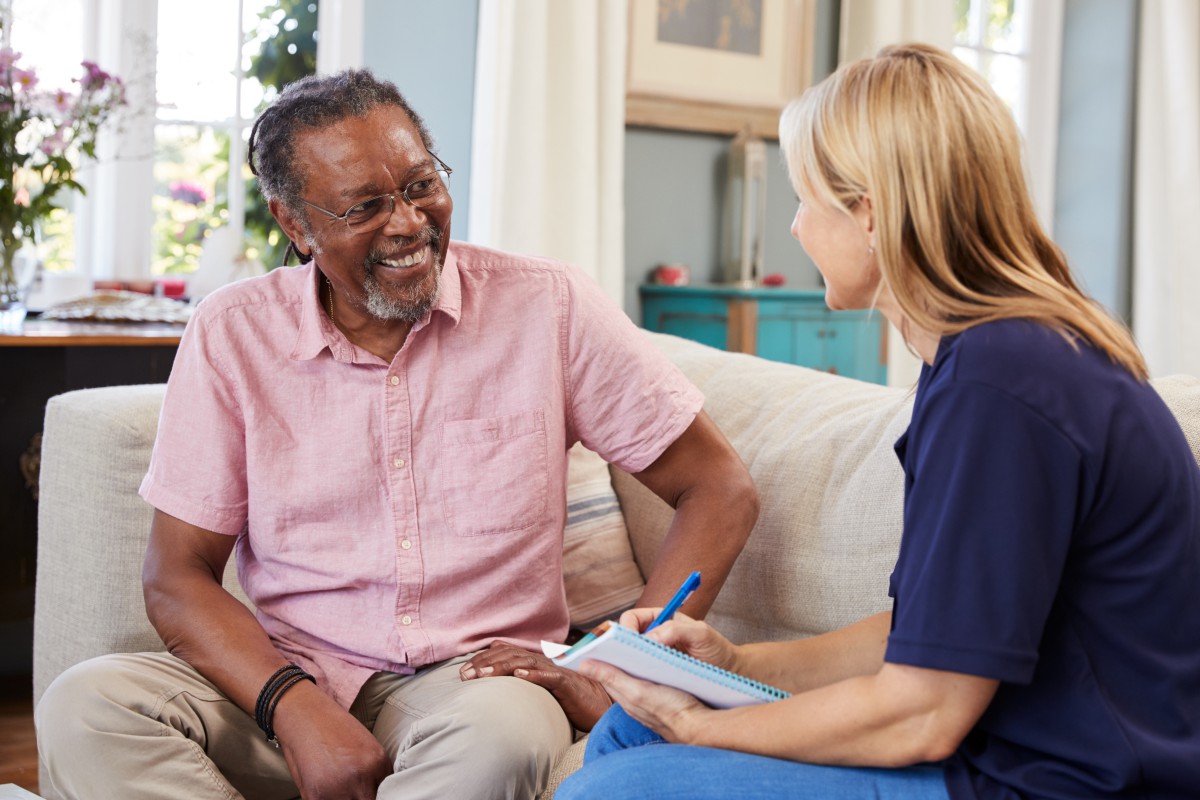

When navigating the complexities of the medical system, healthcare social workers play an invaluable part. These professionals perform important tasks such as walking patients through intake assessments, providing mental health services, and advocating for patients and their families to ensure they receive the care they need. What is a healthcare social worker? A connector and collaborator, ensuring that patients they serve receive all the support available to them.
With an aging and diverse patient population, the demand for social workers specializing in healthcare is growing. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) estimates a 10% increase in healthcare social work roles by 2032. By looking at the roles, responsibilities, and workplaces of healthcare social workers—as well as learning more about the profession’s education requirements and salary potential—individuals who are interested in healthcare social work can better envision what the career path may look like for them.
Where Do Healthcare Social Workers Practice?
From hospitals to substance abuse facilities, healthcare social workers practice a wide variety of settings where patients need assistance navigating the healthcare system and mental health support. Take a look at five settings where healthcare social workers help patients access the best care possible.
Hospitals
Social workers in hospitals serve patients across the lifespan and continuum of health care. They often specialize in a specific department, such as pediatrics, oncology, or emergency/trauma.
Their role often includes:
- Screening and evaluating patients and families
- Performing psychosocial assessments of patients
- Guiding patients and families in understanding the illnesses, conditions, and treatment options
- Helping patients and families transition into a hospital stay or a new department of the hospital
- Educating patients and families on the roles of healthcare team members, levels of health care, rights, and resources
Hospital social workers may also refer patients or families to additional services or community organizations, arrange for financial resources to acquire medications or medical equipment, and coordinate discharge from the hospital. They may also work with fellow healthcare professionals in rehabilitation centers, community organizations, or private practices to ensure continuity of care for patients and their families.
Health Clinics & Outpatient Health Care Settings
Healthcare social workers work in a wide variety of clinics and outpatient facilities. These settings may serve a specific population—such as fertility clinics and dialysis centers—or free-standing primary care clinics like community health centers and school-based health facilities.
The functions of a healthcare social worker in an outpatient or health clinic setting often include:
- Assessing, diagnosing, and treating mental health conditions like depression or anxiety
- Managing cases and coordinating care across facilities and levels of healthcare
- Identifying the need for special services and referring patients to providers
- Educating patients and the community on issues of physical, mental, and emotional health
- Assisting patients with medications, medical devices, transportation, and advance directives
The National Association of Social Workers (NASW) notes that social workers interested in preventative care or prefer a fast-paced environment may thrive in a clinic or outpatient healthcare setting.
Mental Health Clinics and Outpatient Facilities
Healthcare social workers are essential in serving patients seeking mental health treatment. They may work with patients to help them cope with everyday stresses or common mental health struggles such as anxiety or depression. Depending on their training, social workers in these settings may also work with patients facing complex diagnoses like schizophrenia or bipolar disorders.
The job duties of a social worker in a mental health clinic often include:
- Determining client eligibility for treatment
- Assessing bio-psychosocial factors, social histories, and additional factors such as substance use and emotional functioning
- Developing and implementing treatment plans
- Providing therapy to individuals, families, or groups
- Conducting crisis management measures such as safety assessments
Healthcare social workers who want to work at the intersection of physical and mental health may thrive in a mental health clinic. Social workers in these settings often find it especially important to be part of a collaborative team of providers who work well together.
Additional Workplaces for Healthcare Social Workers
Healthcare social workers may also work for:
- Nursing facilities
- Home health care services
- Residential care facilities
- Substance abuse facilities
- Hospice centers
- Private practices
Learn More about Keuka College's Online Master of Social Work
What Does a Healthcare Social Worker Do?
While their job responsibilities vary somewhat across settings and circumstances, most healthcare social workers perform similar tasks in their daily practice. From conducting intake assessments to providing mental health counseling, healthcare social workers engage in meaningful work.
Intake Assessment
Healthcare social workers speak with patients at admission to create a holistic understanding of their social, emotional, and financial needs. Intake assessments start with asking the patient to share their current conditions and describe the treatment and services they are receiving from other organizations. Social workers also ask about factors such as home composition, financial position, and history of mental health conditions.
The intake process provides information necessary for effective referrals and treatment options. Healthcare social workers consult physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to gain a comprehensive picture of the patient’s needs and determine how to meet them.
Each intake assessment produces a list of recommended steps for a patient’s health and well-being. When healthcare social workers ask about monthly finances, for example, they can learn whether or not a patient struggles to pay bills or needs help with filling out benefit applications.
Healthcare systems with complex webs of stakeholders are often inaccessible or difficult to understand for patients. Social workers in healthcare identify and communicate potential opportunities for better lives to patients. Their expertise is particularly helpful for non-English speakers who face language barriers in addition to other obstacles to care.
Mental Health Services
Licensed clinical social workers provide therapy for patients and their families in difficult circumstances. In underserved or rural areas that have shortages of mental health resources, social workers can fill the gap as licensed mental health providers.
Clinical social workers in healthcare settings help patients understand their diagnoses and treatments. They provide therapy for behavioral and substance use disorders identified during treatment. Caregivers including family members and close friends may also receive support from healthcare social workers.
Understanding and accepting an illness can be very challenging for many patients and family members. Social workers can provide tools and techniques for coping with and processing difficult information and traumatic events.
Case Management
The NASW reports that many social workers say they spend more than half of their time on case management responsibilities. In healthcare, case management refers to the process of helping patients navigate the system of social services. It is an evidence-based practice with several components, including assessment, service planning, implementation, and monitoring.
Case management plays a critical role when it comes to ensuring that patients and families receive the care and services they need.. Researchers have found that effective case management increases patient satisfaction, improves patient outcomes, and reduces costs.
Patient Advocacy
The complexity and cost of healthcare can be bewildering for patients and their families. Social workers in healthcare communicate with medical staff and service providers about patient needs and treatment options. They also explain the ins and outs of healthcare interactions in easy-to-understand language.
Social workers in healthcare act as advocates when patients and their family members disagree with their treatment plans. For example, healthcare social workers may assist with appeals for Medicare recipients who felt they were prematurely discharged. The trust built between social workers and patients proves invaluable in this advocacy role.
Education
Patient and family education is a critical component of social work in healthcare. Studies show that the better a patient understands their condition, the more likely they are to be comfortable with their treatment plan and adhere to it. Take cancer patients, for example. Researchers have found that such individuals benefit from knowledge acquisition in myriad ways, including reduced anxiety, improved pain control, and enhanced self-care.
Social workers are invaluable in providing such individuals with accessible information and resources so that they can understand their situation and consider their options.
Referrals
Patients in healthcare settings have a variety of complex needs that often require a group effort to meet. Social workers can enhance patient care and improve their outcomes by making referrals to professionals with the expertise or resources a patient needs.
Examples could include a social worker referring:
- A breast cancer patient to a local nonprofit that facilitates patient discussion groups
- An individual struggling with substance abuse to a rehabilitation center
- A caregiver with financial needs to a community organization that provides groceries and necessities

Becoming a Healthcare Social Worker
While some entry-level roles are available to individuals with a bachelor’s degree in social work (BSW), a master’s in social work (MSW) is typically necessary for specialized positions in clinical settings. BSW and MSW degrees both feature clinical components. While the exact requirements vary by program, accredited BSW degrees must include at least 400 hours of supervised field experience while accredited MSW programs must include at least 900.
Earning an MSW is required for those who want to take the Association of Social Work Boards licensure exam to become a clinical social worker. Other licensing requirements vary by state.
Healthcare Social Worker Salary Potential
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports a mean annual wage of $62,760 for healthcare social workers. The following BLS chart provides further insight into the salary potential for healthcare social workers in Industries with the highest levels of employment of such professionals:
|
Industry |
Employment (1) |
Percent of industry employment |
Hourly mean wage |
Annual mean wage (2) |
|
45,030 |
0.81 |
$ 35.09 |
$ 72,980 |
|
|
22,890 |
1.49 |
$ 32.29 |
$ 67,160 |
|
|
22,450 |
0.79 |
$ 24.84 |
$ 51,660 |
|
|
14,370 |
1.07 |
$ 26.93 |
$ 56,010 |
|
|
13,450 |
1.32 |
$ 32.14 |
$ 66,850 |
Learn More about Keuka College's Online MSW Program
Become a Healthcare Social Worker at Keuka College
Keuka College’s Online MSW trains current social workers and career-changing students for careers in healthcare social work. Students build advanced skills during entirely virtual coursework. Keuka College also assists each MSW candidate in finding field placement opportunities in their communities.
The Traditional MSW track prepares students with bachelor’s degrees in other fields for clinical social work roles. This three-year program requires 60 credits of coursework and 900 field placement hours. Traditional track candidates learn the skills they need for success in courses like:
- Human Behavior & the Social Environment
- Social Work Ethics & Applications in Diversity
- Social Work Practice with Couples and Families
Social work professionals who have already earned BSW degrees are eligible for the Advanced track, which takes less than two years to complete. With 33 credits of coursework and 500 field placement hours, advanced track students build on their BSW foundation in classes such as:
- Advanced Theory for Social Work Practice
- Assessment and Treatment of Trauma
- Group Process
Start your journey as a social worker with Keuka College’s Online MSW program.